
Expert Mathmatician
Polynomials
Distributive Property:
The Distributive Property is when you take a value that is multiplying a number or more in brakets and share that value to each individual value. For example: a(b+c) will change to ab+ac. this works because each value in the brakets will be multiplied by a.
with real numbers we can do: 5(3+x). Using the Distributive Property we will end up with
5 (3 +x)
↓ ↑ ↑
→→ ↑ = 5(3) + 5x
↓ ↑
→→→→→→
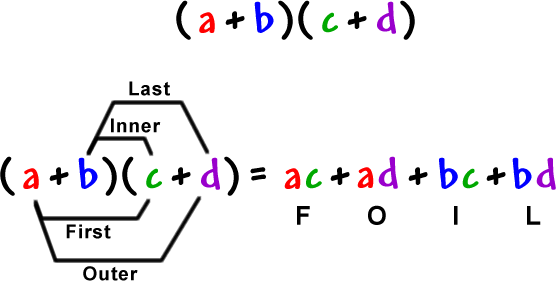
FOIL:
Foil is used when you have two binomial brackets. There are four steps for Foil, hence the name F.O.I.L
-
F : First- You multiply the first diget in the first braket by the first diget of the second braket
-
O: Outside- You multiply the first diget in the first bracket with the second diget of the seconf bracket
-
I : Inner- You multiply the second diget of the first bracket by the first diget of the second bracket
-
L : Last- You multiply the second diget of the first bracket by the second diget of the second bracket
Product and Sum and Difference:
You can convert to and from a given equation using Product and Sum and Difference. For example, (a^2)-(b^2). The two Binomials are being multipled in the brackets and subtracted together. This is when you can use Product and Sum and Difference. The answer you will get will be (a+b)(a-b). This is correct because you can use FOIL to check.
(a+b)(a-b)
=a^2-ab+ab-b^2
=(a^2)-(b^2)
However you can only use this formula when the two products are being subtracted
Perfect Square Trinomials:
Perfect Square Trinomials is a formula that can be used when the last two numbers of a Trinomial can be square rooted and if the two numbers that are square rooted multiplied by two equal the middle term.
a^2+2ab+b^2
Example:
4x^2+8x+16
- 4 and 16 are perfect squares.
4=2
16=4
- 8x is a product of 2x*4
=(2x+4)^2
*the numbers are subtracted or added together depending on if the middle term is a negative or not. In this case the middle term is a positive number so we will add.
Therefore the equation 4x^2+8x+16 is a Perfect Square Trinomial.